|
|
|
|
|
|
|
News & Views item - October 2009 |
![]() 2009 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine Awarded to Elizabeth Blackburn,
Carol Greider and Jack Szostak. (October 6, 2009)
2009 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine Awarded to Elizabeth Blackburn,
Carol Greider and Jack Szostak. (October 6, 2009)
The Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institutet has announced that the 2009 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine has been awarded jointly to Elizabeth H. Blackburn, Carol W. Greider and Jack W. Szostak for the discovery of "how chromosomes are protected by telomeres and the enzyme telomerase".
 Elizabeth
H. Blackburn has US and Australian citizenship. She was
born in 1948 in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. After undergraduate studies
at the University of Melbourne, she received her PhD in 1975 from the
University of Cambridge, England, and was a postdoctoral researcher at
Yale University, New Haven, USA. She was on the faculty at the
University of California, Berkeley, and since 1990 has been professor of
biology and physiology at the University of California, San Francisco. Elizabeth
H. Blackburn has US and Australian citizenship. She was
born in 1948 in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. After undergraduate studies
at the University of Melbourne, she received her PhD in 1975 from the
University of Cambridge, England, and was a postdoctoral researcher at
Yale University, New Haven, USA. She was on the faculty at the
University of California, Berkeley, and since 1990 has been professor of
biology and physiology at the University of California, San Francisco. |
 Carol
W. Greider is a US citizen and was born in 1961 in San
Diego, California, USA. She studied at the University of California in
Santa Barbara and in Berkeley, where she obtained her PhD in 1987 with
Blackburn as her supervisor. After postdoctoral research at Cold Spring
Harbor Laboratory, she was appointed professor in the department of
molecular biology and genetics at Johns Hopkins University School of
Medicine in Baltimore in 1997. Carol
W. Greider is a US citizen and was born in 1961 in San
Diego, California, USA. She studied at the University of California in
Santa Barbara and in Berkeley, where she obtained her PhD in 1987 with
Blackburn as her supervisor. After postdoctoral research at Cold Spring
Harbor Laboratory, she was appointed professor in the department of
molecular biology and genetics at Johns Hopkins University School of
Medicine in Baltimore in 1997. |
 Jack
W. Szostak is a US citizen. He was born in 1952 in London,
UK and grew up in Canada. He studied at McGill University in Montreal
and at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, where he received his PhD
in 1977. He has been at Harvard Medical School since 1979 and is
currently professor of genetics at Massachusetts General Hospital in
Boston. He is also affiliated with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Jack
W. Szostak is a US citizen. He was born in 1952 in London,
UK and grew up in Canada. He studied at McGill University in Montreal
and at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, where he received his PhD
in 1977. He has been at Harvard Medical School since 1979 and is
currently professor of genetics at Massachusetts General Hospital in
Boston. He is also affiliated with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
|
The Nobel Committee for Physiology or Medicine summarises the work:
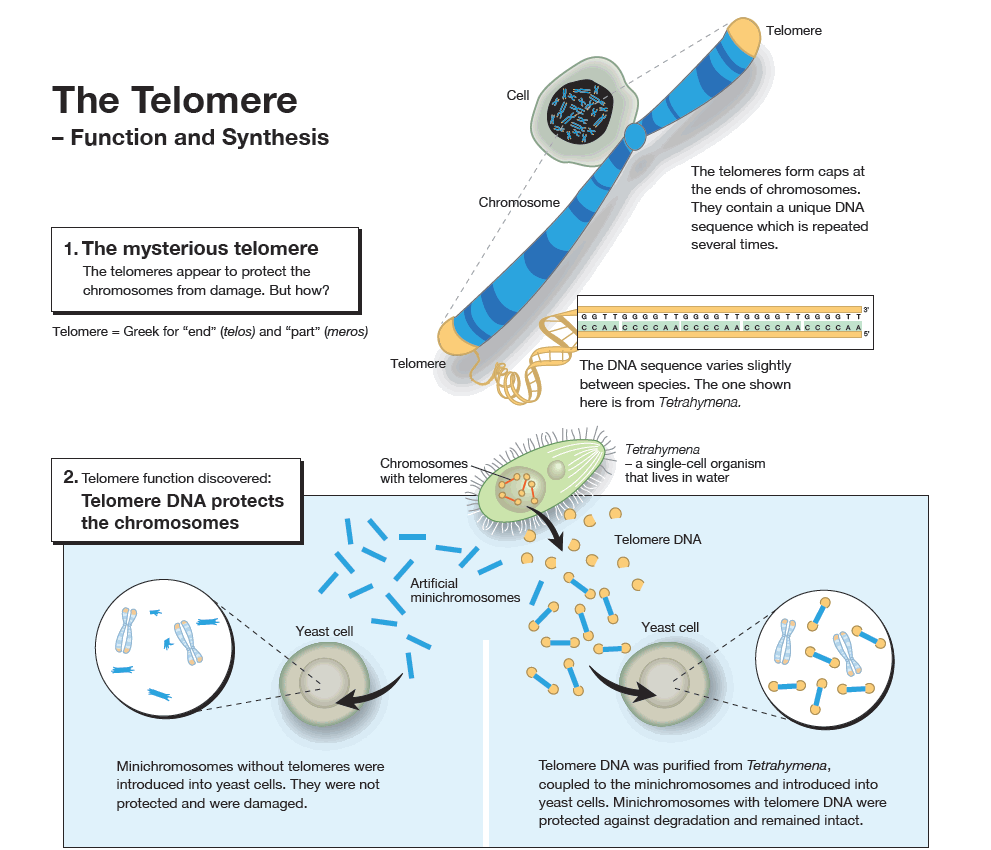
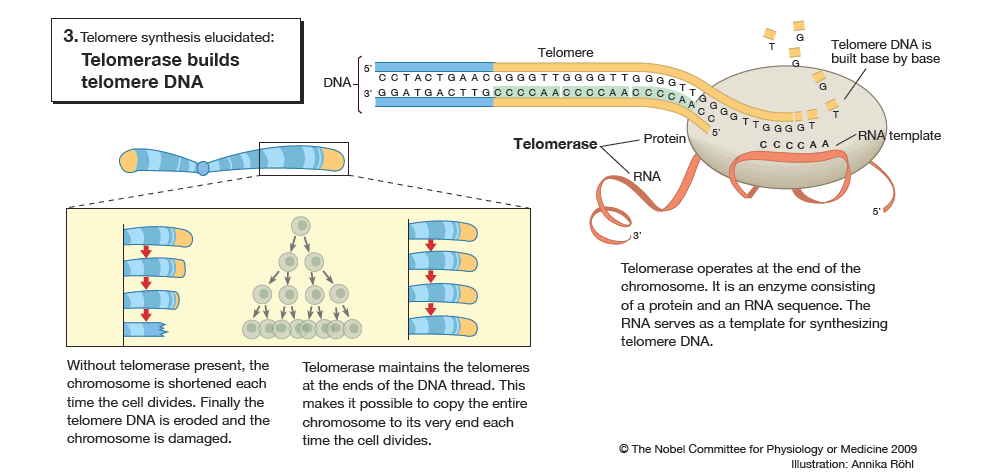
This year's Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded to three scientists who have solved a major problem in biology: how the chromosomes can be copied in a complete way during cell divisions and how they are protected against degradation. The Nobel Laureates have shown that the solution is to be found in the ends of the chromosomes – the telomeres – and in an enzyme that forms them – telomerase.
The long, thread-like DNA molecules that carry our genes are packed into chromosomes, the telomeres being the caps on their ends. Elizabeth Blackburn and Jack Szostak discovered that a unique DNA sequence in the telomeres protects the chromosomes from degradation. Carol Greider and Elizabeth Blackburn identified telomerase, the enzyme that makes telomere DNA. These discoveries explained how the ends of the chromosomes are protected by the telomeres and that they are built by telomerase.
If the telomeres are shortened, cells age. Conversely, if telomerase activity is high, telomere length is maintained, and cellular senescence is delayed. This is the case in cancer cells, which can be considered to have eternal life. Certain inherited diseases, in contrast, are characterized by a defective telomerase, resulting in damaged cells. The award of the Nobel Prize recognizes the discovery of a fundamental mechanism in the cell, a discovery that has stimulated the development of new therapeutic strategies.