|
|
|
|
|
|
|
News & Views item - August 2006 |
![]() Institute of Higher Education, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Publishes its 2006
Top 500 Research Universities. (August 19, 2006)
Institute of Higher Education, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Publishes its 2006
Top 500 Research Universities. (August 19, 2006)
Begun in 2003 the Institute of Higher Education's rankings of the world's research universities has become the de facto standard despite more recent entries from The Times and the entry this month from Newsweek.
The Institute describes its ranking criteria and weighting:
We rank universities by several indicators of academic or research performance, including alumni and staff winning Nobel Prizes and Fields Medals, highly cited researchers, articles published in Nature and Science, articles indexed in major citation indices, and the per capita academic performance of an institution.
For each indicator, the highest scoring institution is assigned a score of 100, and other institutions are calculated as a percentage of the top score. The distribution of data for each indicator is examined for any significant distorting effect; standard statistical techniques are used to adjust the indicator if necessary.
Scores for each indicator are weighted as shown below to arrive at a final overall score for an institution. The highest scoring institution is assigned a score of 100, and other institutions are calculated as a percentage of the top score. An institution's rank reflects the number of institutions that sit above it.
See footnote below for definitions of "Indicators"
Click here to access the ranking's Website.
The top 10 once again show Harvard University as the "Roger Federer" of research universities being given a total point score of 100 with Cambridge and Stanford battling it out for second spot with scores of 72.6 and 72.5 respectively.
|
University |
Score |
| Harvard University |
100 |
|
University of Cambridge |
72.6 |
|
Stanford University |
72.5 |
|
University of California - Berkeley |
72.1 |
|
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) |
69.7 |
|
California Institute of Technology (Cal Tech) |
66.0 |
|
Columbia University |
61.8 |
|
Princeton University |
58.6 |
|
University of Chicago |
58.6 |
|
University of Oxford |
57.6 |
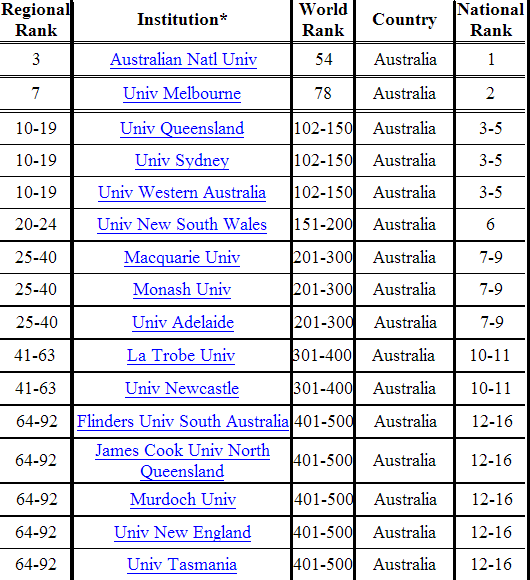
Australia still hasn't placed in the top 50 but again gets two places in the top 100, and a total of 16 of its universities in the list of 500.
The total point scores for Australia's top two are ANU = 30.8 and Melbourne University = 26.4.
Universities ranked below 100 are not assigned total scores.
Definition of Indicators
Alumni. The total number of the alumni of an institution winning Nobel
Prizes and Fields Medals. Alumni are defined as those who obtain bachelor,
Master's or doctoral degrees from the institution. Different weights are set
according to the periods of obtaining degrees. The weight is 100% for alumni
obtaining degrees in 1991-2000, 90% for alumni obtaining degrees in 1981-1990,
80% for alumni obtaining degrees in 1971-1980, and so on, and finally 10% for
alumni obtaining degrees in 1901-1910. If a person obtains more than one
degrees from an institution, the institution is considered once only.
Award. The total number of the staff of an institution winning Nobel
prizes in physics, chemistry, medicine and economics and Fields Medal in
Mathematics. Staff is defined as those who work at an institution at the time
of winning the prize. Different weights are set according to the periods of
winning the prizes. The weight is 100% for winners in 2001-2005, 90% for
winners in 1991-2000, 80% for winners in 1981-1990, 70% for winners in
1971-1980, and so on, and finally 10% for winners in 1911-1920. If a winner is
affiliated with more than one institution, each institution is assigned the
reciprocal of the number of institutions. For Nobel prizes, if a prize is
shared by more than one person, weights are set for winners according to their
proportion of the prize.
HiCi. The number of highly cited researchers in broad subject
categories in life sciences, medicine, physical sciences, engineering and
social sciences. These individuals are the most highly cited within each
category. The definition of categories and detailed procedures can be found at
the website of Institute of Scientific Information.
N&S. The number of articles published in Nature and Science between
2001 and 2005. To distinguish the order of author affiliation, a weight of
100% is assigned for corresponding author affiliation, 50% for first author
affiliation (second author affiliation if the first author affiliation is the
same as corresponding author affiliation), 25% for the next author
affiliation, and 10% for other author affiliations. Only publications of
article type are considered.
SCI. Total number of articles indexed in Science Citation
Index-expanded and Social Science Citation Index in 2005. Only publications of
article type are considered. When calculating the total number of articles of
an institution, a special weight of two was introduced for articles indexed in
Social Science Citation Index.
Size. The weighted scores of the above five indicators divided by the
number of full-time equivalent academic staff. If the number of academic staff
for institutions of a country cannot be obtained, the weighted scores of the
above five indicators is used. For ranking 2006, the numbers of full-time
equivalent academic staff are obtained for institutions in USA, UK, Japan,
South Korea, Czech, China, Italy, Australia, Netherlands, Sweden, Switzerland,
Belgium, Slovenia, New Zealand etc.